Opiate based drugs come in many forms, most of which carry pain-relieving properties. Both natural opiates and synthetically made forms produce the same effects on the brain and body.
Natural opiates, such as morphine, opium and codeine, originate from the opium poppy seed plant. Synthetic opiates may contain natural ingredients as well as man-made compounds capable of intensifying opiate effects.
When taken on a regular basis, the effects of opiate based drugs can extend well beyond their initial pain-relieving properties. Opiate based drugs target certain key brain chemical functions that regulate the body’s central nervous system.
With long-term use, a person can easily become physically and psychologically dependent on opiates. Ultimately, opiate based drugs have the potential to take over essential brain functions, especially when abused on an ongoing basis.
Pain-Relieving Mechanisms
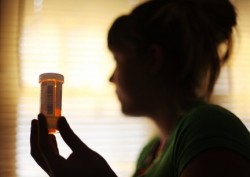
Opiates are taken for pain relief, though many people become addicted and take them to get high.
The human brain produces its own natural pain-relieving chemicals known as endorphins. Endorphins and opiate based drugs produce similar effects within the brain’s chemical processes.
When ingested, opiates trigger the release of endorphin chemicals from designated cell receptor sites in the brain. These chemicals slow signal transmission rates between nerve cells throughout the body. These interactions account for the reduction in pain a person experiences.
With ongoing use, opiates gradually alter the brain’s natural endorphin production abilities to the point where endorphin secretion functions come to depend on opiate effects, according to the U. S. National Library of Medicine. This cycle of dependency continues for as long as person keeps using the drug.
Opiates not only slow down pain signal transmission rates, but also every bodily process regulated by the central nervous system. In actuality, the endorphins involved in pain reduction are serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine, all essential brain neurotransmitter chemicals. As a result, the effects of opiate based drugs have the potential to disrupt a person’s entire physiological make-up over time.
Tolerance Effects
Tolerance effects have to do with how the brain becomes less sensitive to the effects of opiate based drugs with continued use. With each successive dose, opiates place an inordinate strain on brain cell receptor site functions. Eventually, cell sites start to deteriorate from overuse.
As brain cell structures weaken, they require larger doses of the drug to function normally. This means, pain sensations will persist unless a person increases his or her dosage amount. Brain tolerance levels will continue to increase for as long as a person keeps using.
Dependency & Addiction
Along with their pain-relieving effects, opiate based drugs produce certain desirable aftereffects, such as relaxation, euphoria and calm. These aftereffects combined with the brain’s increasing tolerance levels can easily drive a person to keep increasing his or her dosage amounts in order to sustain the drug’s desired effects.
Over time, this process essentially cripples brain functions as cell sites undergo progressive deterioration. In effect, the brain becomes physically dependent on opiates and cannot function normally in the absence of the drug.
Before too long, users start to develop a psychological dependency as opiates “reconfigure” the brain’s reward center. When this happens, opiates become a primary motivation in a person’s life, driving his or her thoughts, behaviors and daily priorities.
 Tips for Overcoming Opium Addiction -
Opioid Addiction is a chronic addiction that is lifelong. Opiates are highly addictive and a tolerance is built with each use. As the tolerance is built, the body also then goes through a certain amount of withdrawal after each use and those symptoms increase as the dose needed to achieve the desired high does. As ...
Tips for Overcoming Opium Addiction -
Opioid Addiction is a chronic addiction that is lifelong. Opiates are highly addictive and a tolerance is built with each use. As the tolerance is built, the body also then goes through a certain amount of withdrawal after each use and those symptoms increase as the dose needed to achieve the desired high does. As ...  How Painful are the Symptoms of Opium Withdrawal? -
Opium withdrawal can be a slow, painful, and difficult process. These are the symptoms most associated with opium withdrawals and their varying degrees of pain. Factors Influencing Withdrawal Everyone reacts differently to opium withdrawal based on certain factors specific to each experience. The level of drug use will strongly affect the severity of the withdrawal ...
How Painful are the Symptoms of Opium Withdrawal? -
Opium withdrawal can be a slow, painful, and difficult process. These are the symptoms most associated with opium withdrawals and their varying degrees of pain. Factors Influencing Withdrawal Everyone reacts differently to opium withdrawal based on certain factors specific to each experience. The level of drug use will strongly affect the severity of the withdrawal ...  5 Potential Dangers of Opiate Prescription Drugs -
As far as pain relief agents go, opiate prescription drugs offer the most effective treatment approach. These drugs naturally interact with the body’s own pain management system promoting fast relief from pain symptoms. These same interactions play a central role in the high abuse and addiction potential associated with opiate prescription drugs. Opiate prescription drugs ...
5 Potential Dangers of Opiate Prescription Drugs -
As far as pain relief agents go, opiate prescription drugs offer the most effective treatment approach. These drugs naturally interact with the body’s own pain management system promoting fast relief from pain symptoms. These same interactions play a central role in the high abuse and addiction potential associated with opiate prescription drugs. Opiate prescription drugs ...  Am I a Good Candidate for Naltrexone? -
Naltrexone can be a beneficial treatment option for many recovering opiate addicts, however it is not meant for everyone.
Am I a Good Candidate for Naltrexone? -
Naltrexone can be a beneficial treatment option for many recovering opiate addicts, however it is not meant for everyone.  How Do I Know If Someone I Love Is Abusing Opium? -
Opium is an incredibly intense narcotic with strong side effects. When abused over time, it can lead to addiction. If you think someone you know is frequently abusing opium, it is better to find out soon so you can help them seek treatment and recover. Call now to have Opium.org help you to find rehab ...
How Do I Know If Someone I Love Is Abusing Opium? -
Opium is an incredibly intense narcotic with strong side effects. When abused over time, it can lead to addiction. If you think someone you know is frequently abusing opium, it is better to find out soon so you can help them seek treatment and recover. Call now to have Opium.org help you to find rehab ...